Alcohol is often considered a recreational drug and in Scotland, according to a survey in 2018, 53% of 13 year olds and 70% of 15 year olds who had ever tried alcohol, reported to have been drunk at least once.

🍺Alcohol is classified as a drug which affects the Central Nervous System. The CNS (Central Nervous System) is made up of neurons (nerves which carry information). If you cut your finger the information passes up the spinal cord to the brain so action can be taken.
🧪Levels of alcohol intoxication are measured in Blood alcohol Content (BAC)
When alcohol in the bloodstream reaches the CNS it can delay and inhibit neurotransmitters (the messenger molecules) from passing information along (the brain doesn't know you are injured so cannot heal you).
🧠After 1 to 4 alcoholic drinks (0.01 to 0.12 BAC) the brain is already affected by the alcohol and as well as reaction times becoming slower, judgement is affected and mood and behaviour< may change.
😵💫Once a BAC of 0.18 to 0.30 has been reached emotional disorientation and confusion occurs and memory is affected. The area of the brain responsible for moving short-term memory to long-term memory is the hippocampus. Alcohol can block this transfer, resulting in gaps in the memory called alcohol-induced blackouts.
⚕️Consumption of more alcohol beyond this stage (BAC of 0.25 and 0.40) can result in alcohol poisoning and death. At this drunken stupour stage, the motor functions are severely impaired and any response to stimuli is absent or extremely slow. At this stage seek medical help< as the risk of hypothermia, arrhythmia, seizures or respiratory arrest are high.
💀At levels of BAC above this (0.35+ BAC) the result is severe impairment to respiration, circulation, temperature regulation, reflexes and motor response. This inevitably leads to coma and ultimately death if life functions are not sustainable.
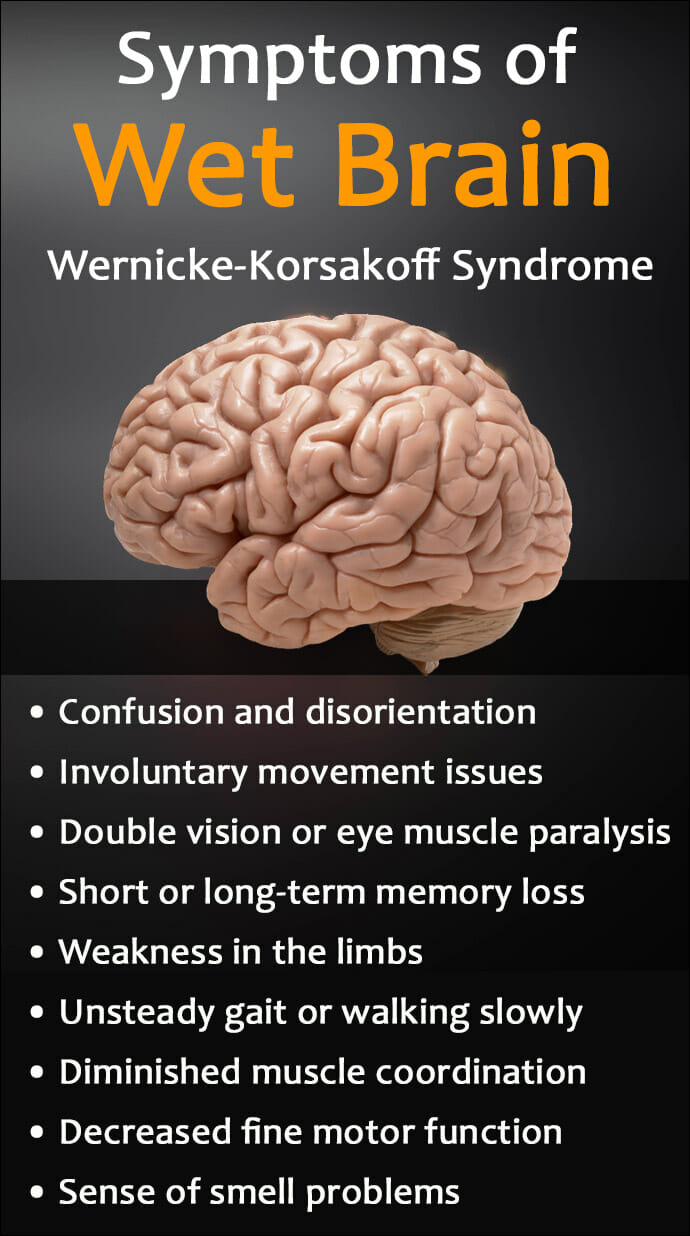
Long term alcohol abuse can cause Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome (Wet Brain). This occurs as a result of a deficiency of thiamine (vitamin B1).Alcohol not only blocks an enzyme which converts thiamineto something the body can use, it also hinders absorption of the vitamin affecting the liver functions.